Unlock the power of visual storytelling! This guide delves into the art of effectively using images to communicate compelling narratives. We’ll explore key principles, practical techniques for image selection and editing, and strategies for seamless integration into various design layouts. Learn how to transform static images into dynamic components of your visual communication strategy.
From understanding the foundational principles of visual storytelling to mastering image editing and layout techniques, we’ll equip you with the skills to create visually captivating and impactful designs. Whether you’re designing a website, brochure, or social media campaign, this guide provides a practical roadmap to success.
Understanding Visual Storytelling Principles
Visual storytelling leverages the power of images to communicate narratives effectively, transcending linguistic barriers and engaging audiences on an emotional level. It’s about crafting a compelling sequence of visuals that convey a message, evoke feelings, and leave a lasting impression. Images, far from being mere decorations, become integral components of the story itself, driving the narrative forward and enhancing understanding.
Effective visual storytelling relies on several core principles. First, strong imagery is crucial; each image should be carefully selected to contribute meaningfully to the overall narrative. Second, a clear narrative arc is essential; the sequence of images should guide the viewer through a logical progression of events or ideas. Third, the emotional impact of the images must be considered; visuals should evoke the desired feelings in the audience, whether it’s joy, sadness, excitement, or intrigue. Finally, the visual style should be consistent with the tone and message of the story, creating a cohesive and impactful experience.
Examples of Visual Storytelling Across Media
Successful visual storytelling is evident across diverse media. Advertising campaigns often employ compelling imagery to associate products with specific lifestyles or emotions. Consider a classic Coca-Cola advertisement showing friends sharing a laugh over ice-cold drinks on a sunny afternoon; the image instantly conveys feelings of happiness and togetherness, subtly linking these positive emotions to the product. Film, naturally, is a powerful medium for visual storytelling, with iconic scenes from movies like “Citizen Kane” or “Casablanca” immediately conjuring up specific narratives and emotional responses. Infographics, on the other hand, use visual elements to simplify complex data, making information more accessible and engaging. A well-designed infographic on climate change might use striking visuals to illustrate the impact of rising sea levels, making abstract data more concrete and emotionally impactful.
A Visual Narrative: Three Images
Let’s construct a simple visual narrative using three images.
Image 1: A young woman sits alone at a park bench, head bowed, rain falling around her. The image is muted in color, emphasizing the feeling of sadness and isolation. The setting is somber, mirroring her internal state.
Image 2: The same woman is now standing in a brightly lit art studio, surrounded by vibrant colors and canvases. A slight smile plays on her lips as she holds a paintbrush. The color palette shifts to warm, inviting tones. This image represents a shift in her emotional state – a tentative step towards hope and self-expression.
Image 3: The woman stands proudly before a finished painting, a vibrant and expressive piece. Sunlight streams in from a window, illuminating her confident posture. The painting itself is the culmination of her journey, reflecting her newfound strength and resilience. This image showcases triumph and the power of creative expression.
Image Layout and Storytelling
The arrangement of these images significantly impacts the narrative flow.
This table layout, with three images in the first three columns and an empty column for responsiveness, allows for a clear, sequential presentation of the story. The linear progression mirrors the emotional arc, leading the viewer from sadness to hope and finally to triumph. A different layout, perhaps placing Image 2 between Images 1 and 3, could subtly alter the narrative’s pacing and emotional impact. A responsive layout ensures that the images adapt well to different screen sizes, maintaining the visual coherence of the story regardless of the device used.
Selecting and Using Images Effectively

Choosing the right images is crucial for effective visual storytelling. The visuals you select should not only be aesthetically pleasing but also directly support and enhance your narrative, guiding the viewer’s understanding and emotional response. A poorly chosen image can detract from your message, while a well-chosen one can significantly amplify its impact. This section will explore best practices for image selection and utilization.
High-Quality Image Selection and Alignment with Message
Selecting high-quality images involves considering several factors beyond mere visual appeal. The image should directly relate to the narrative’s content and tone. For example, an image of a bustling city street would be inappropriate for a story about quiet contemplation. Resolution should be high enough to avoid pixelation when displayed at the intended size. The image’s composition, lighting, and subject matter should all contribute to the overall message. Consider the mood you want to evoke – is it excitement, calmness, seriousness, or something else? The chosen image should reflect that mood effectively. For instance, a vibrant, brightly lit image would convey excitement, while a muted, dimly lit image might suggest a more somber tone.
Image Resolution, Format, and Licensing
Image resolution, measured in pixels (e.g., 1920×1080), dictates the image’s sharpness and clarity. Low-resolution images will appear blurry when enlarged. Different platforms have different resolution requirements; for instance, images for print media require significantly higher resolution than those for web use. Common image formats include JPEG (best for photographs), PNG (best for graphics with transparency), and GIF (best for animations). Understanding licensing is critical to avoid copyright infringement. Images are typically licensed under Creative Commons (various levels of permissibility) or require purchase from stock photo sites. Always check the license before using an image to ensure you are compliant with its terms of use. Using unlicensed images can lead to legal repercussions and damage your credibility.
Comparison of Image Types and Suitability
Photographs offer realism and immediacy, making them ideal for conveying authentic experiences or showcasing products. Illustrations, on the other hand, allow for greater artistic control and can be used to simplify complex concepts or create a unique visual style. Icons are small, symbolic images frequently used for user interface elements or to represent ideas concisely. The choice of image type depends heavily on the specific context and the message you aim to convey. For example, a scientific report might benefit from photographs and charts, while a children’s book might use vibrant illustrations. A website might employ a mix of photographs, illustrations, and icons to achieve a balanced and visually engaging design.
Step-by-Step Image Editing Guide
Improving an image’s visual appeal and relevance involves several steps. First, color correction can significantly enhance the image’s mood and impact. Tools allow adjusting brightness, contrast, saturation, and white balance to achieve a more balanced and visually appealing result. Next, cropping removes unwanted elements and focuses attention on the most important parts of the image. Careful cropping can dramatically improve composition and storytelling. Finally, resizing adjusts the image’s dimensions to fit the intended space, ensuring optimal display without distortion or loss of quality. For example, a photograph of a landscape might be cropped to emphasize the mountain range, and then resized to fit a website banner. Software such as Adobe Photoshop or GIMP provides the necessary tools for these editing tasks. Remember to save your edited images in the appropriate format and resolution for your intended use.
Integrating Images into Design Layouts
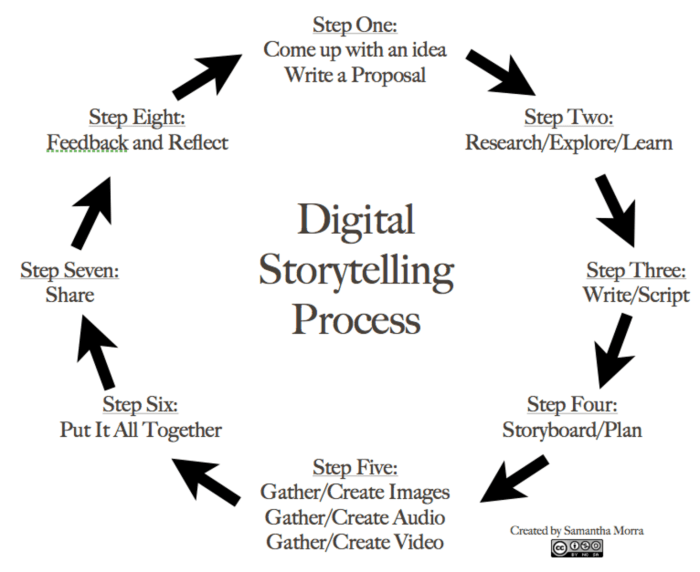
Successful visual storytelling hinges not only on selecting impactful images but also on strategically integrating them into your design layouts. The placement and treatment of images significantly influence the overall message and user experience, whether you’re crafting a website, a brochure, or a social media post. Effective image integration enhances readability, guides the eye, and ultimately strengthens your narrative.
The techniques for incorporating images vary greatly depending on the platform and desired effect. Websites often employ hero images—large, captivating visuals dominating the top of the page—to immediately grab attention and set the tone. Brochures, on the other hand, might utilize a grid layout, arranging images alongside text blocks in a structured manner to present information concisely. Social media platforms demand visually striking, concise imagery, often optimized for specific aspect ratios and screen sizes. Consider the platform’s inherent limitations and strengths when choosing your approach.
Whitespace Utilization for Visual Balance and Hierarchy
Whitespace, or the negative space around images and text, is a crucial element in achieving visual balance and establishing a clear hierarchy. Insufficient whitespace can lead to a cluttered and overwhelming design, making it difficult for the viewer to process information. Conversely, excessive whitespace can feel empty and lack focus. The ideal balance involves strategically using whitespace to separate elements, create visual breathing room, and guide the viewer’s eye through the design. A well-designed layout uses whitespace to emphasize key images and text, creating a visual hierarchy that directs attention to the most important information first. For instance, a website homepage might use ample whitespace around a hero image to draw immediate attention to it, while smaller images within the body copy are surrounded by less whitespace to maintain a sense of visual rhythm.
Common Design Mistakes and Their Solutions
A common mistake is using low-resolution images that appear pixelated or blurry, significantly detracting from the overall aesthetic. The solution is simple: always use high-resolution images appropriate for the intended display size. Another frequent error is inconsistent image sizing and placement, leading to a visually jarring experience. Maintaining consistent image dimensions and applying a unified style guide will remedy this. Overusing filters or effects can also be detrimental, resulting in images that are overly processed and lack authenticity. A more natural approach, emphasizing image quality over excessive manipulation, is generally preferred. Finally, ignoring accessibility considerations, such as using sufficient color contrast between images and text, is a crucial oversight. Ensuring adequate contrast improves readability for users with visual impairments.
Creating Visually Appealing Layouts with Text and Images
A well-designed layout combines text and images harmoniously to enhance comprehension and engagement. Consider the following example of a website homepage:
This homepage features a large hero image showcasing a vibrant landscape, immediately setting a positive and inviting tone. Below, a concise headline clearly communicates the website’s purpose. The subsequent text is broken into easily digestible paragraphs, interspersed with smaller, related images that support the text’s message. Whitespace is generously used to separate sections and maintain visual clarity.
The call to action button is prominently placed, encouraging user engagement. The overall design is clean, balanced, and easy to navigate, ensuring a positive user experience.
This approach demonstrates the power of thoughtful image placement and whitespace management in creating a visually appealing and effective website homepage.
Last Recap

Mastering the art of visual storytelling through image design is a journey of continuous learning and experimentation. By understanding the principles Artikeld here – from selecting high-quality images and employing effective editing techniques to integrating them seamlessly within your layouts – you can elevate your design work to new heights. Remember, the most impactful designs are those that tell a story, resonate emotionally, and leave a lasting impression on your audience. Embrace experimentation and watch your visual narratives flourish.